In the digital age, securing applications is more critical than ever. Robust authentication mechanisms are vital for protecting user data and ensuring secure access. This is where Spring Security and Keycloak come into play, offering powerful solutions for secure authentication in web applications.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into an authentication demo project that showcases the integration of Spring Security with Keycloak. This post will walk you through this GitHub project, providing insights into its setup, functionality, and practical applications.
Overview of the Project
Our project is a practical demonstration of authentication mechanisms using Spring Boot 2.7 and Keycloak 21. It's divided into three key components:
- auth-server: This is a Keycloak server set up using Docker, which manages user authentication.
- bootcamp-service: A Spring Boot application demonstrating form-based and OAuth2 authentication.
- library-service: Another Spring Boot application, this time focusing on JWT-based authentication.
Getting Started: Prerequisites
Before diving in, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- Docker and Docker Compose for starting preconfigured Authentication Server.
- Java 11 and Maven for running the Spring Boot applications.
These tools are essential for setting up and running the project smoothly.
Step-by-Step Guide to Running the Project
- Start the Keycloak server: Navigate to the auth-server directory and execute
docker compose up. This fires up the Keycloak authentication server. - Run the Applications: In the bootcamp-service and library-service directories, use
mvn spring-boot:runto start each application. - Access the applications: Once running, you can access:
- bootcamp-service at http://localhost:8080
- library-service at http://localhost:8081
Deep Dive: Technical Description
At the heart of our project is the Spring Security's filter chain, a mechanism that intercepts requests for authentication and authorization. It’s like a security checkpoint, ensuring only valid requests get through.

bootcamp-service
Bootcamp service provides two types of authentication:
1. Form-based Authentication
To configure form-based authentication, add .formLogin() to the SecurityConfig class. This enables the default login page provided by Spring Security.
2. OAuth2 Authentication
To configure OAuth2 authentication, add .oauth2Login() to the SecurityConfig class.
bootcamp-service acts as oauth2 client, it has dependency to spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client which provides the necessary classes to authenticate and authorize users.
In spring security, OAuth 2.0 Login is implemented by using the Authorization Code Grant
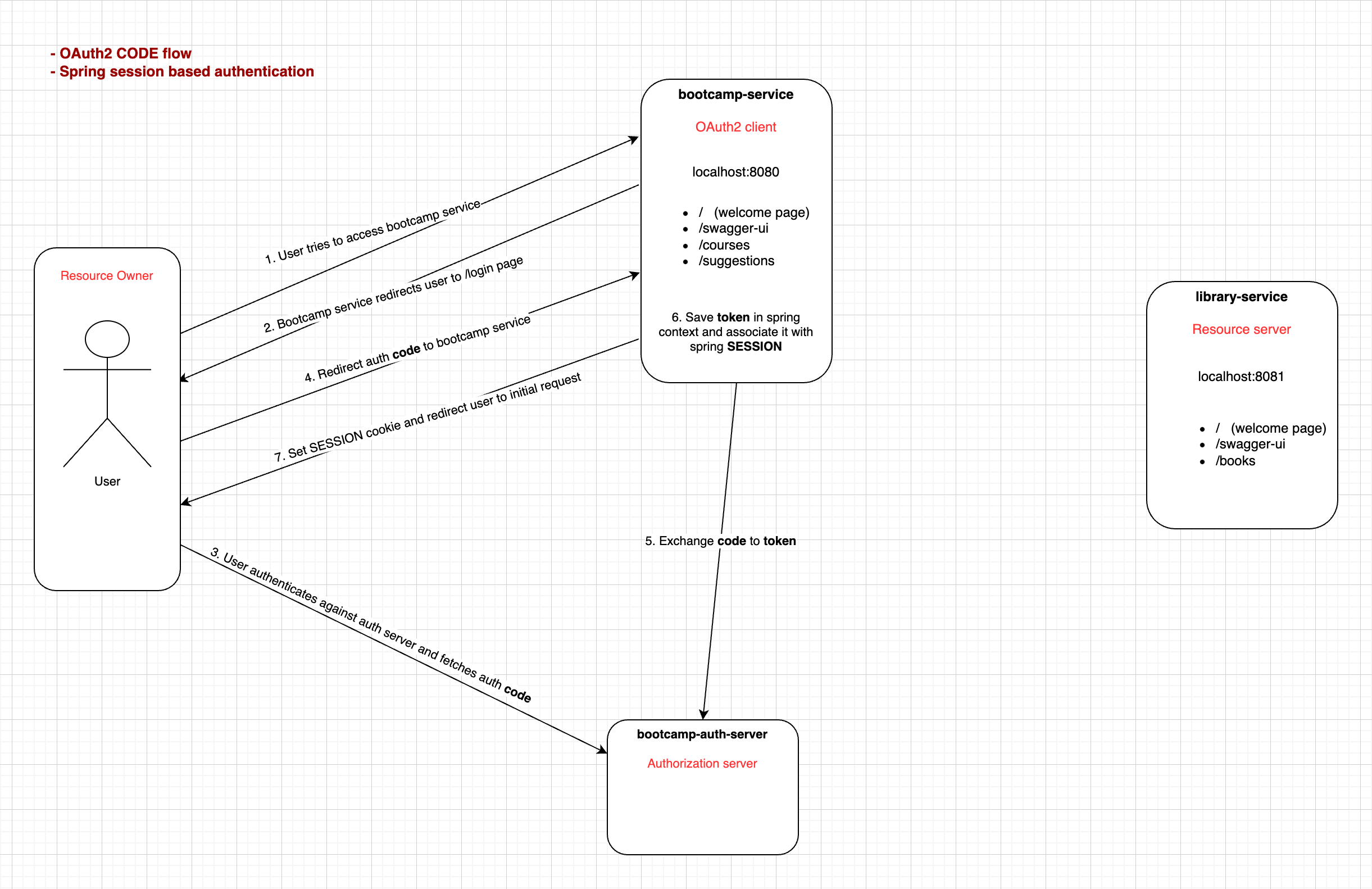
Diagram: Code Flow - AUTHORIZATION_CODE
The following diagram shows the code flow, which is used in the bootcamp-service application. Note that, bootcamp service saves the access token in the session, so that it can be used in subsequent requests.
library-service
In the library-service module of our project, we utilize JWT (JSON Web Tokens) for authentication. JWT is a stateless security mechanism where a server generates a secure, encoded token for each authenticated user. This token, containing the user's identity and privileges, is verified on each request without the need to maintain a session state. This method is highly favored for its simplicity and the way it enables secure, stateless interactions in web applications.
To configure JWT authentication, add .oauth2ResourceServer() to the SecurityConfig class.
library-service acts as resource server, it has dependency to spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server which provides the necessary classes to validate the token and authorize users.
High level overview of JWT authentication in Spring Security:

In the diagram above, library-service replaces:
- the default
(3) JwtDecoderwith a custom implementation, which uses the public key of the Keycloak server to validate the token. - the default
(4) JwtAuthenticationConverterwith a custom implementation, which converts the JWT claims to spring security authorities.
Diagram: JWT Authentication
The following diagram shows the JWT authentication flow, which is used in the library-service application. Library service is stateless, so it doesn't save the access token, instead it validates it in every request.

Keycloak Setup
Keycloak is used for user management and authentication. The auth-server module includes a pre-configured Keycloak instance. Access the Keycloak admin console at http://localhost:8888/auth using the provided credentials.
For newcomers to Keycloak, check the Keycloak Documentation for more information on setup and configurations.
Users and Roles
This demo involves three roles:
STUDENT- Allowed to perform GET operations in both applications.TEACHER- Permitted for modification and deletion operations in thebootcamp-service.LIBRARY_ADMIN- Authorized for modification and deletion operations in thelibrary-service.
In the Keycloak server, there are three users:
jon- Jon Snow - assigned theSTUDENTrole.james- James Zanti - assigned theTEACHERrole.laura- Laura Admin - assigned theLIBRARY_ADMINrole.
Additionally, the bootcamp-service has two built-in users:
student- assigned theSTUDENTrole.teacher- assigned theTEACHERrole.
All users have the password set as test.
Additional Resources
- Spring Security Reference
- The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework
- Using JWTs as Authorization Grants
- Spring Boot and OAuth2
- Keycloak
This project is a stepping stone into the world of secure authentication using Spring Security and Keycloak. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, understanding these mechanisms is crucial in today's security-conscious world.

